Phytoremediation of Emerging Contaminants in Wetlands: Unlocking a Sustainable Solution for Environmental Restoration

In the face of increasing environmental pollution, traditional remediation methods often fall short of addressing the challenges posed by emerging contaminants—compounds that are not easily removed using conventional techniques. Phytoremediation, the use of plants to remove or transform contaminants from the environment, has emerged as a promising solution, particularly in wetlands, which offer unique advantages for contaminant biodegradation.
Wetlands: Nature's Contaminant Filters

Wetlands are complex ecosystems that play a crucial role in maintaining water quality and biodiversity. Their unique characteristics, including high moisture content, diverse plant communities, and microbial activity, make them well-suited for phytoremediation.
- High moisture content: Wetlands provide a moist environment that supports the growth of plants with extensive root systems, which are essential for absorbing and degrading contaminants.
- Diverse plant communities: Wetlands host a variety of plant species, each with unique physiological and biochemical traits that enable them to tolerate and degrade specific contaminants.
- Microbial activity: The anaerobic conditions in wetland soils foster the growth of specialized microorganisms that contribute to contaminant degradation.
Emerging Contaminants: A Growing Threat
Emerging contaminants are a diverse group of compounds that have recently been identified as posing significant environmental and health risks. These contaminants include pharmaceuticals, personal care products, flame retardants, and industrial chemicals, which are often persistent, mobile, and toxic.

Traditional remediation methods, such as activated carbon adsorption or chemical oxidation, are often ineffective or prohibitively expensive for removing emerging contaminants. Phytoremediation offers a cost-effective and sustainable alternative, particularly in wetlands, where the natural processes of plant uptake, transformation, and microbial degradation can be harnessed to remove these contaminants from the environment.
Phytoremediation in Wetlands: Mechanisms and Applications
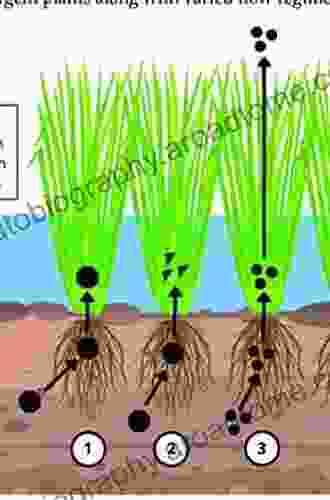
Phytoremediation in wetlands involves the use of plants to absorb, degrade, or volatilize contaminants from water and soil. The mechanisms involved in phytoremediation include:
- Phytoextraction: Plants absorb contaminants through their roots and transport them to their above-ground tissues, where they can be stored or volatilized.
- Phytodegradation: Plants use enzymes to break down contaminants into less harmful substances.
- Phytostabilization: Plants immobilize contaminants in the soil, preventing their movement and bioavailability.
- Phytovolatilization: Plants take up contaminants and release them into the atmosphere through transpiration.
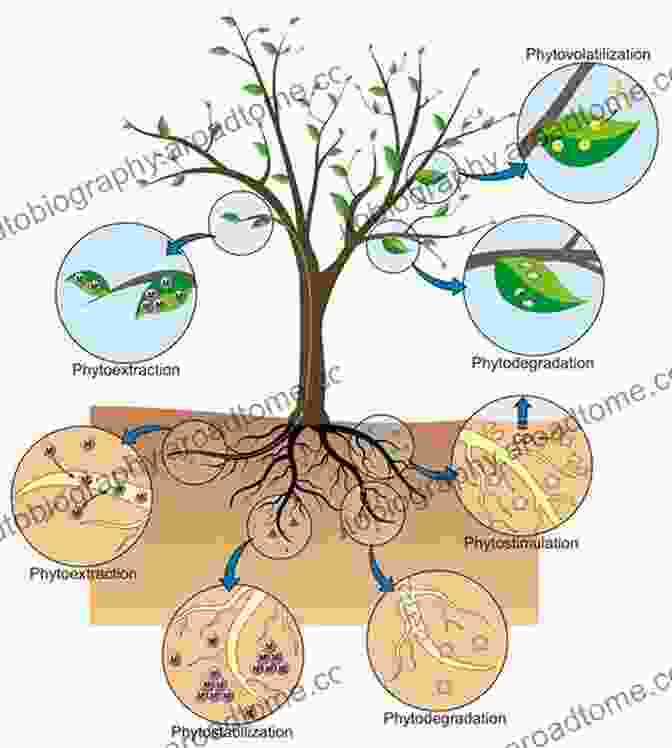
The effectiveness of phytoremediation in wetlands depends on several factors, including the type of contaminant, the plant species used, and the environmental conditions. Research has demonstrated the potential of various plant species for phytoremediation of emerging contaminants in wetlands, including:
- Phragmites australis (Common Reed): This plant is known for its ability to tolerate high levels of heavy metals and organic pollutants.
- Typha latifolia (Broadleaf Cattail): This plant has been shown to effectively remove pharmaceuticals and personal care products from water and soil.
- Salix species (Willows): Willow trees have been used to phytoextract heavy metals and organic compounds from contaminated sites.
Benefits of Phytoremediation in Wetlands
Phytoremediation in wetlands offers several advantages over traditional remediation methods:
- Cost-effective: Phytoremediation is generally less expensive than other remediation techniques, as it relies on natural processes rather than energy-intensive equipment.
- Sustainable: Phytoremediation does not generate hazardous waste or cause environmental disruption, making it a more sustainable approach to remediation.
- Aesthetically appealing: Wetlands can be designed to be aesthetically pleasing, providing recreational and habitat benefits in addition to contaminant removal.
- Bioremediation: Wetlands support diverse microbial communities that contribute to contaminant degradation, enhancing the overall efficiency of phytoremediation.
Case Studies and Future Prospects
Numerous successful case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of phytoremediation in wetlands for removing emerging contaminants. For example, a study in the Netherlands showed that a wetland system planted with Phragmites australis effectively removed over 90% of pharmaceuticals from wastewater.
Research is ongoing to optimize phytoremediation techniques and identify new plant species for removing specific emerging contaminants. Advancements in molecular biology and genetic engineering hold promise for developing plants with enhanced contaminant degradation capabilities.
Phytoremediation of emerging contaminants in wetlands offers a promising and sustainable solution for environmental remediation. By harnessing the natural processes of plant uptake, transformation, and microbial degradation, wetlands can be transformed into cost-effective and aesthetically pleasing filters that remove harmful contaminants from our environment.
As research continues to advance, phytoremediation is expected to play an increasingly significant role in addressing the challenges posed by emerging contaminants. By embracing this innovative and sustainable approach, we can protect our water resources, soil quality, and human health for generations to come.
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Louisa Taylor
Louisa Taylor Tom Bowers
Tom Bowers 2003rd Edition
2003rd Edition Wayne Gladstone
Wayne Gladstone Oscar Harkavy
Oscar Harkavy Nicki Scully
Nicki Scully Kathy Hoopmann
Kathy Hoopmann Richard J Leider
Richard J Leider David J Unger
David J Unger Christopher T Nelson
Christopher T Nelson Margaret Gilbert
Margaret Gilbert Julie Hatfield
Julie Hatfield Susan Carrell
Susan Carrell Zoran Nikolic
Zoran Nikolic Todd Anton
Todd Anton Tycho Press
Tycho Press Nicola Perullo
Nicola Perullo Erik Skare
Erik Skare J W Clark
J W Clark Missy Miller
Missy Miller
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Jan MitchellUnveiling Underwater Damage with Image-Based Precision: A Revolutionary Guide...
Jan MitchellUnveiling Underwater Damage with Image-Based Precision: A Revolutionary Guide...
 Richard SimmonsUnveiling the Intricacies of Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) Devices: A...
Richard SimmonsUnveiling the Intricacies of Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) Devices: A... Spencer PowellFollow ·12k
Spencer PowellFollow ·12k Darnell MitchellFollow ·2.8k
Darnell MitchellFollow ·2.8k Chance FosterFollow ·16.1k
Chance FosterFollow ·16.1k Banana YoshimotoFollow ·10.9k
Banana YoshimotoFollow ·10.9k Grayson BellFollow ·18k
Grayson BellFollow ·18k Eliot FosterFollow ·2.9k
Eliot FosterFollow ·2.9k Johnny TurnerFollow ·14.2k
Johnny TurnerFollow ·14.2k Shaun NelsonFollow ·19.5k
Shaun NelsonFollow ·19.5k

 Nathan Reed
Nathan ReedProgress In Complex Systems Optimization Operations...
This book presents...

 Duncan Cox
Duncan CoxHSK Chinese Grammar: The Ultimate Guide to Master Chinese...
HSK Chinese...

 Owen Simmons
Owen SimmonsDevelopment and Applications in Policy Support...
Unveiling the Transformative...

 Travis Foster
Travis FosterTransform Emotions Into Energy To Achieve Your Greatest...
Do you feel like your...

 Joe Simmons
Joe SimmonsUnlocking the Frontiers of Artificial Intelligence: Delve...
In the annals of artificial...